What is Autism?
“Autism” (or “autism spectrum disorder” also known as “ASD”) refers to a disorder currently diagnosed through symptoms, which involve difficulties in social interaction, verbal and nonverbal communication and repetitive behaviors.
The DSM-5, updated in 2013, uses two key categories of symptoms for diagnosing autism:
persistent deficits in social communication and social interaction across multiple contexts, and
restricted, repetitive patterns of behaviors, interest, or activities, manifested by at least two of the following:
stereotyped or repetitive movements, use of objects, or speech;
insistence on sameness, inflexible adherence to routines, or ritualized patterns of behavior;
highly restricted, fixated interests of abnormal intensity or focus;
hyper- or hypo-reactivity to sensory input or unusual interests in sensory aspects of the environment.
Symptoms for autism typically appear between 10-18 months of age. Unfortunately, the average age of diagnosis is 4-years-old. A diagnosis is usually made by a developmental pediatrician. Typically, there is a waiting list for appointments to get this diagnosis.
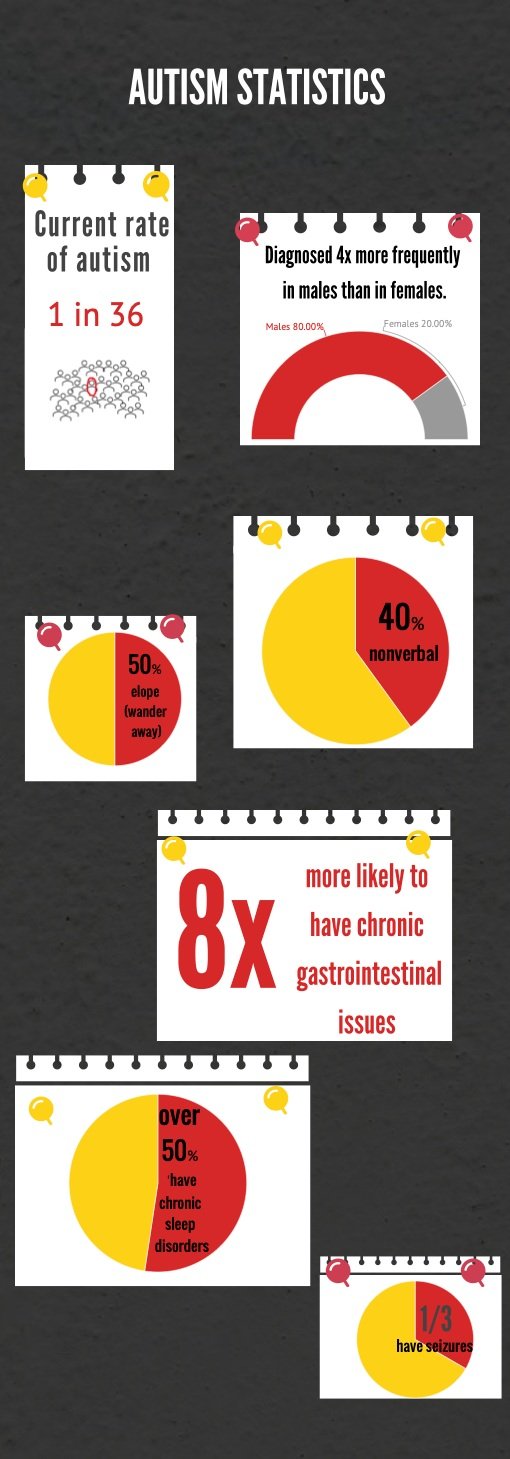
The rate of autism has increased dramatically over the past two decades. The current rate, as of March 2023, is 1 in 36 children. Although we now have better diagnostics and increased awareness, these improvements do not account for the marked increase. We applaud those who are researching the causes while we focus on the necessary services.